Polyether vs. Polyester TPU: A Technical Comparison Guide for Film Selection
To the naked eye, Polyether and Polyester TPU films look identical. However, for product engineers, choosing the wrong one can be catastrophic.
While Polyester (Ester) is known for its toughness, it has a fatal weakness: water. Polyether (Ether), on the other hand, withstands humidity and microbes. This guide breaks down the molecular battle of Ether vs. Ester to help you make the right decision.

1. The Core Difference: Chemistry 101
The difference lies in the soft segment of the polymer chain. This molecular distinction determines how the material reacts to the environment.
Polyether TPU (Ether)
Based on Ether bonds. These molecules are chemically stable and "hydrophobic," naturally repelling water attack and resisting fungal growth.
View Ether TPU Products →Polyester TPU (Ester)
Based on Ester bonds. Tightly packed molecules provide high physical strength but are susceptible to breaking down when water attacks the linkage (Hydrolysis).
2. Head-to-Head Performance Battles
Round 1: Hydrolysis Resistance (Water & Humidity)
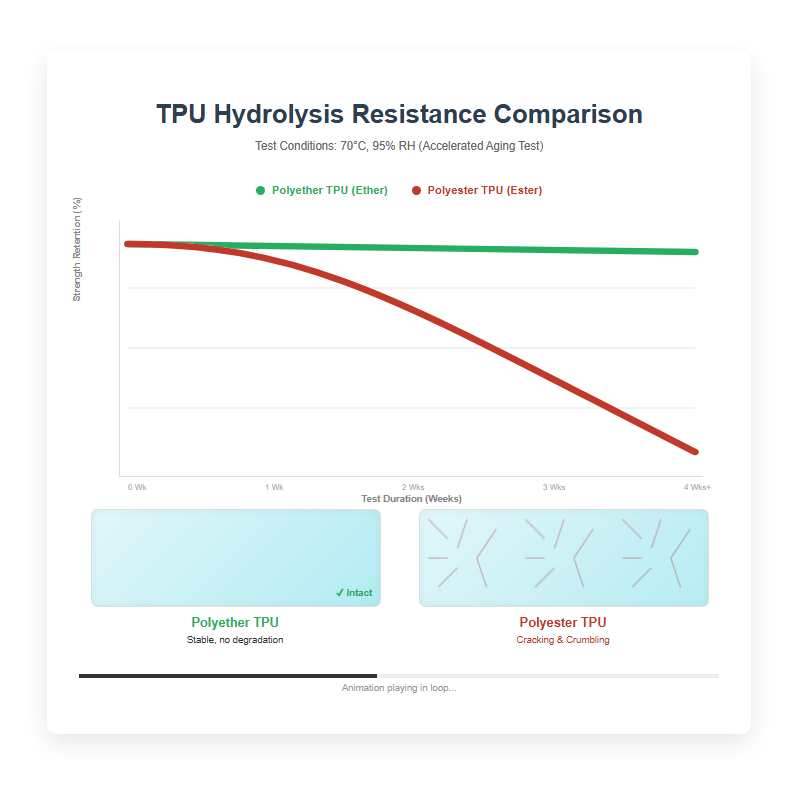
Winner: Polyether TPU
This is the biggest differentiator. If you put Polyester TPU in a humid environment (or submerge it in water), the molecular chains will break down over time, causing the film to crack and crumble. Polyether TPU is virtually immune to hydrolysis.
Round 2: Abrasion & Tensile Strength
Winner: Polyester TPU
Polyester molecules are more tightly packed, giving them superior physical toughness. If your product needs to withstand constant scraping against rough surfaces (like a shoe upper), Polyester offers better wear resistance.
Round 3: Chemical & Oil Resistance
Winner: Polyester TPU
When it comes to industrial chemicals, fuels, and oils, Polyester is the stronger candidate. It resists swelling and degradation when in contact with grease. Polyether TPU, while stable, may swell slightly if exposed to certain hydrocarbon solvents for extended periods.
3. The "Cheat Sheet": Comparison Table
| Polyester (Ester) TPU Standard Industrial Grade | Polyether (Ether) TPU Recommended for Automotive/Medical |
|---|---|
| Hydrolysis Resistance: Limited; susceptible to hydrolysis over extended periods in humidity. | Hydrolysis Resistance: Excellent; chemically stable against moisture. |
| Abrasion Resistance: Outstanding; highest toughness and scratch resistance. | Abrasion Resistance: Good; sufficient for most non-industrial applications. |
| Chemical & Oil Resistance: Superior; ideal for contact with fuels and grease. | Chemical & Oil Resistance: Moderate; may swell with prolonged exposure. |
| Low-Temperature Flexibility: Good; usually flexible down to -20°C. | Low-Temperature Flexibility: Superior; remains soft down to -40°C or lower. |
4. Application Guide: When to Use Which?
✅ Choose Polyether (Ether) If Your Product:
- Will be exposed to direct water, humidity, or sweat.
- Requires biocompatibility (Medical devices).
- Will be used in extreme cold weather (Winter gear).
Ideal for: Water ball, Medical Dressings, Hydration Bladders.

✅ Choose Polyester (Ester) If Your Product:
- Needs maximum tear strength and abrasion resistance.
- Will be in contact with oils, fuels, or solvents.
- Is intended for dry environments where cost efficiency is key.
Ideal for: Conveyor Belts, Shoe Uppers, Industrial Aprons.

Still Unsure Which Formulation Fits Your Project?
Selecting the wrong TPU base can lead to product recalls. As a source factory, GREEN TPU can customize both Polyether and Polyester films to your exact specs.


